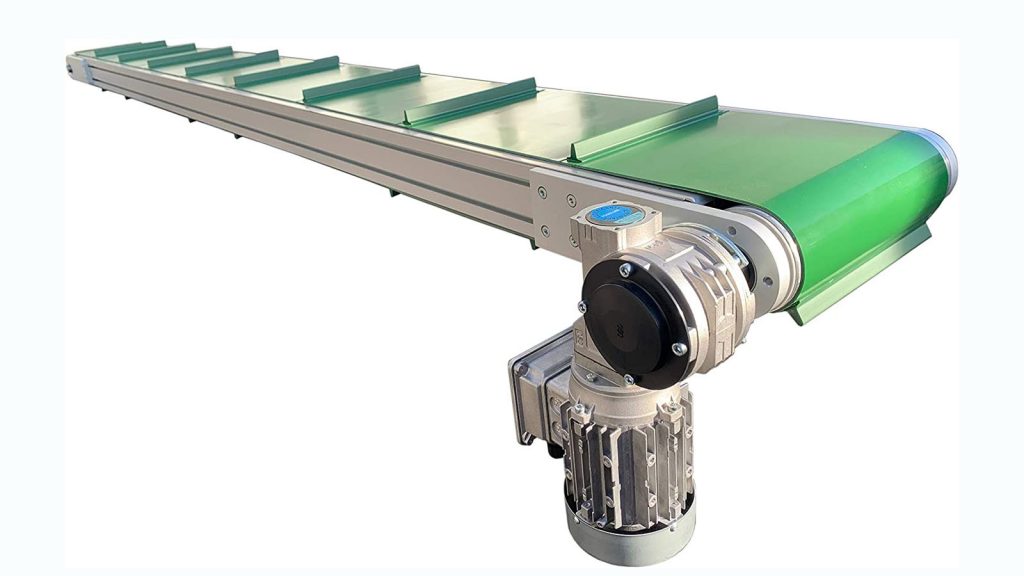
Conveyor
A conveyor is an industrial machine used in production lines to continuously move materials from one place to another. It has a transport belt that carries products up or down to their next location. Conveyors are frequently used in industries such as food, automotive, electronics, and steel.
Applications of the Conveyor Machine:
The conveyor is a machine used to continuously move materials in many industries. It has a belt that can be flat or slanted, carrying materials to their destination. The applications of this machine include:
Transporting materials in production lines
Moving goods in warehouses
Transporting food, dairy products, vegetables, etc.
Moving automotive parts, electronics, plastics, etc.
Transporting postal packages, retail goods, etc.
Use in power generation systems
Use in the mining and cement industry for transporting sand, limestone, coal, etc.
Advantages of Using a Conveyor:
Increased Speed and Efficiency: The conveyor boosts production and product transfer speeds due to its continuous and uninterrupted movement.
Time and Cost Savings: It also saves time and is cost-effective, as it requires minimal maintenance and repair.
Product Protection: The conveyor allows products to be transported steadily without the risk of damage.
Adjustability: The conveyor is adjustable in dimensions, speed, shape, and packaging material, making it suitable for all industries.
Eliminating Errors in Processes: By using a conveyor, human errors in production and product transfer processes are minimized.
Types of Conveyors:
Tubular Conveyor: A conveyor with a tubular enclosure designed to transport material in a continuous and undisturbed manner.
Angled Conveyor: Unlike a flat conveyor, this type has an angled bend.
Belt Conveyor: Uses a plastic or rubber belt of a specific width and length to transport products in various ways.
Roller Conveyor or Screw Conveyor: Products are placed on rollers or screws and moved continuously.
Multilevel Conveyor: Moves products across multiple levels in a continuous flow.
Here, we want to provide a more detailed description of screw conveyors.
Screw Conveyor:
A screw conveyor is a mechanized device used in various industries for transporting materials. Owing to its specific structure and function, it is accepted as one of the most imperative tools for material transfer in production lines.
Types of Screw Conveyors:
Horizontal Screw Conveyors: Horizontal screw conveyors are the most common type of screw conveyor. They are used in a wide range of designs, sizes, distances, and construction materials to move bulk goods from one location to another. In this machine, a screw is placed horizontally inside a tube, and with the rotation of the screw, materials continuously move forward.
Inclined Screw Conveyors: Inclined screw conveyors operate from horizontal levels up to a 45-degree incline. This machine is also known as a vertical screw conveyor when the incline angle exceeds 45 degrees. As the incline angle increases, the transfer capacity decreases, and a more powerful motor is needed to move the materials. The transfer performance is influenced by the incline angle, material properties, screw blade shape, and screw pitch. For optimal output from screw conveyors, it is recommended to use the minimum possible incline.
Shaftless Screw Conveyors: This conveyor type features a shaftless spiral, which facilitates smooth material movement without clogging. It’s particularly suited for transferring materials with high moisture content. These conveyors efficiently handle sticky or slow-moving bulk materials and are flexible, allowing for easy relocation within the factory layout due to the lack of internal bearings.
Vertical Screw Conveyors: Vertical screw conveyors are excellent for lifting bulk materials at steep or vertical angles. When the incline exceeds 45 degrees, it’s classified as a vertical screw conveyor. They offer a cost-effective and efficient solution with few moving parts, capable of handling dry to semi-fluid materials at up to 170 cubic meters per hour. These conveyors can lift materials up to 10 meters high and can be fully enclosed to protect against dust or vapor.
Care and Maintenance of Conveyor Systems:
Cleaning the Conveyor: Regularly clean the conveyor with a washing solution to prevent dust buildup.
Surface Examination: Check for scratches or unevenness on the conveyor surface.
Roller Inspection: Periodically dismantle and reassemble rollers to ensure proper function.
Repairing: Replace broken parts and adjust worn-out components as needed.
Replacing Parts: Swap out parts that cannot be repaired.
Electrical Systems Inspection: Check the conveyor’s electrical systems for any malfunctions or errors.
Employee Training: Train employees on the proper operation and maintenance of the conveyor.